
What is Facial Recognition?
Facial recognition is a method of identifying or verifying a person’s identity by analyzing an image of their face via machine learning models. The technology can be used to identify people in real time using photos or videos. Facial recognition is currently being used in various fields, primarily for biometric access control, but also for other applications such as augmented reality.
How Does Facial Recognition Work?
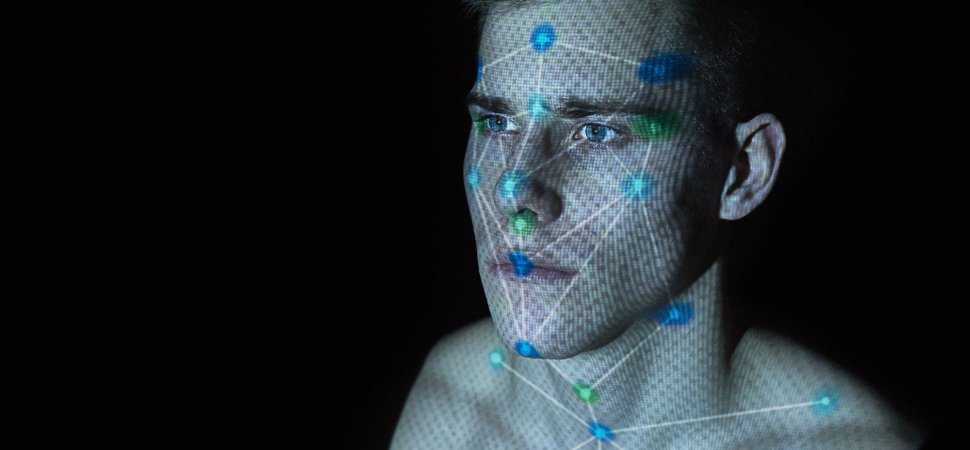
Face recognition uses artificial intelligence algorithms to detect faces and separate them from a background. The algorithm typically starts by searching for the human eye and then searches for the eyebrows, nose, mouth, nostrils, and iris. Once all facial features are captured, they are further validated using large datasets of positive and negative images to confirm that they are human faces.
Common techniques for face recognition include feature-based, shape-based, knowledge-based, and template matching. Each of these methods has advantages and disadvantages:
- Feature-based methods detect faces based on features such as eyes and nose. Results from this method may vary due to noise and light.
- Appearance-based methods also use statistical analysis and machine learning to match features of facial images.
- Knowledge-based methods recognize faces according to predefined rules. This can be difficult given the effort required to define these rules.
- Template matching methods detect faces by comparing the image to previously stored facial patterns or features and correlating the results. However, this approach cannot accommodate changes in size, posture or shape.
5 Little-Known Applications of Face Recognition
Diagnosing Genetic Disorders
Facial recognition can help diagnose rare genetic diseases, especially mild genetic disorders. For example, at Nemours Children’s Hospital in Delaware, clinicians struggled to diagnose patients with abnormal symptoms. The hospital used Face2Gene, a facial recognition mobile app developed by one of the hospitals’ researchers. The app scans patient photos, analyzes faces using 130 landmarks, and uses machine learning to match detected facial features to features of rare genetic disorders.
The application generated a list of potential diagnoses and assigned a probability score to each diagnosis. With the help of Face2Gene, medical staff discovered a rare case of a genetic condition, the Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome.
Face2Gene isn’t the first app to rely on facial recognition to diagnose rare diseases. It is one of the most popular. App developers report using the product to evaluate 250,000 patients and help identify 7,000 genetic conditions.
Fleet Management
Fleet management can use facial recognition to notify unauthorized individuals of attempted access to a vehicle and deter theft. While traditional solutions such as noisy alarms are effective, they do not always deter decisive criminals. In the future, vehicles could simply be driven without human supervision to avoid theft.
A primary cause of accidents is careless use of mobile phones, and so another use of facial recognition technology is to detect when a driver’s eyes are off the road. Fleet vehicles can also be made safer by training mobile apps to detect drunk or tired drivers.
IoT Access Control
Security-based facial recognition applications are entering the IoT space. The main use of facial recognition in the home is as an intrusion system to detect if criminals have broken into a home. Advances in this area can be extended to access control devices. In the future, homeowners will be able to open their front doors without using traditional door locks and keys, replacing today’s “smart” locking solutions that still rely on a mobile device to unlock them.
Additionally, the technology could work in parallel with existing facial recognition technologies built into social networks like Facebook. Users can virtually connect Facebook events to an IoT device to automatically access invited visitors who have previously received RSVPs.
Increasing Learning Engagement

Facial recognition systems can interpret a variety of emotions. Researchers report that analyzing facial micro-expressions of students, such as raising eyebrows and squeezing eyelids, can help highlight boredom, confusion, joy, frustration, surprise, and other emotions. This is useful for professors and course designers.
For example, during a lecture, a professor can assess the emotional state of attendees and determine which parts of the lecture stimulate or inhibit interest. Gaining insight into student engagement allows teachers to tailor lessons to better reflect student preferences and provide a more personalized learning experience. However, the use of AI for emotion detection today is mostly experimental.
Customer Verification

As financial services become almost completely digital, it makes sense to follow the customer verification process. Using electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) solutions, financial institutions can now take their customer onboarding process entirely online. Many eKYC solutions use fingerprints as an authentication method, but facial recognition could be a viable alternative.
Conclusion
In this article, I explained the basics of face recognition and showed 5 applications of face recognition:
- Diagnosing genetic disorders—Facial recognition can help diagnose rare genetic diseases, especially mild genetic disorders.
- Fleet management—Fleet management can use facial recognition to notify unauthorized individuals of attempted access to a vehicle and deter theft.
- IoT access control—in the future, homeowners will be able to open their front doors without using traditional door locks and keys.
- Increasing learning engagement—gaining insight into student engagement allows teachers to tailor lessons to provide a more personalized learning experience.
- Customer verification—using electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) solutions, financial institutions can now take their customer onboarding process entirely online.
I hope this will be useful as you explore the exciting world of facial recognition technology.




