Engineers are the unsung heroes of modern civilization. But what do engineers do? And how did they become so important? There are many different engineering disciplines, such as mechanical engineering and civil engineering. Mechanical engineers work on anything that moves — cars and airplanes and medical devices like artificial hearts or prosthetic limbs—civil engineers design buildings and bridges and water treatment facilities and waste management systems.
They are the masterminds behind the machines, gadgets like the linear actuator, and other incredible inventions that help us live our lives. Engineering involves solving practical problems using scientific principles and math. Engineers apply their knowledge of math, science, and technology to design solutions to real-world problems. They take a systematic approach to problem-solving by breaking it into manageable parts.
1. Engineers design running Shoes
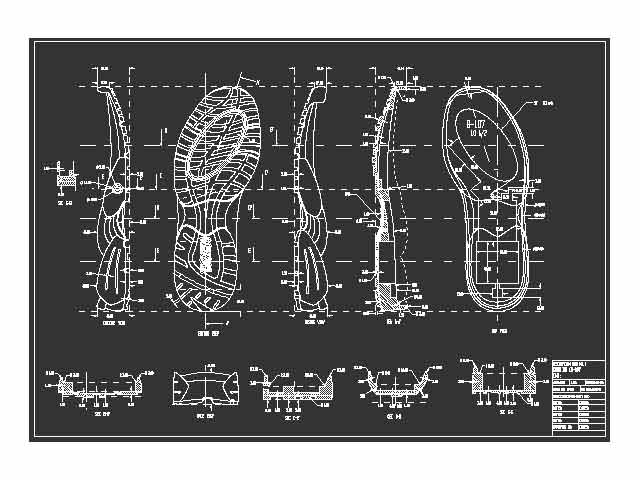
Running shoes are designed by engineers and built with the support of biomechanics experts. A good pair of running shoes will help you prevent injury, improve performance and get the most out of your workouts. That’s why it’s important to invest in a quality pair of running shoes that fit your feet properly. The best running shoes for you are comfortable, supportive, lightweight, and flexible enough for your footstrike type.
2. The Ferris Wheel is one of the greatest engineering wonders

George Washington Gale Ferris Jr. designed it for the Columbian Exposition in Chicago, Illinois. The Ferris Wheel is also known as the big wheel, a misnomer since it’s a large structure composed of multiple wheels.
It was originally designed to carry passengers from the ground level to the top of a hill at an amusement park or fairgrounds at about 50 feet (15 m). However, as time passed, the Ferris Wheel became more elaborate and sophisticated, with some reaching heights well over 250 feet (76 m).
Ferris Wheels are also used as a symbol of commemoration and celebration, such as at military bases during parades, Independence Day celebrations, and sporting events like baseball games, often referred to as “big tops.
3. An Engineer invented the Snowboard

Jake Burton Carpenter designed the first snowboard at his company, which he founded after dropping out of high school to work for his father’s construction company. The snowboard he designed was made from plywood and had no binding attached; instead, riders would wear ski boots with bindings on them and attach their feet to these bindings using straps around their ankles (similar to how skiers attach their feet to their skis).
This meant that when they fell off the board while riding down the hill, they would fall straight down instead of backward like they do today when they slip off their boards while riding down hills.
4. Engineers make Interactive Television possible
Before interactive TV, viewers had little control over what they saw on their televisions. You might think that your TV remote control is just a simple device for changing channels and adjusting volume. But it’s an incredibly complex piece of technology, with thousands of tiny transistors inside, which must be programmed exactly right for it to work properly.
Engineers were responsible for making it possible for viewers to change channels by simply clicking a button rather than tuning their televisions manually (which was very difficult). This programming is done by engineers using computers – who would otherwise be working on something much more important than your television.
5. Microchips double power

Microchips are made of silicon, and for many years, that meant they could double their power every two years. This was known as Moore’s Law, and it held for decades. But in the last few years, it’s become harder to keep doubling the number of transistors on a chip. There are several reasons for this.
Manufacturers are trying to cram more and more transistors onto each chip to make the same kind of products with less electricity while still getting more done.
If you want to keep making your chips faster, you have to get rid of all sorts of heat — which is getting harder and harder.
6. Photoelectric effect

This is one of Einstein’s most famous discoveries – he proved that light could behave like particles and waves (some people say this means he was right before anyone else). The photoelectric effect shows how the sunlight hits objects such as leaves or glass and knocks electrons off them into space, creating an electric current that can be harnessed by a generator or battery (which are themselves inventions made possible by other engineering marvels).